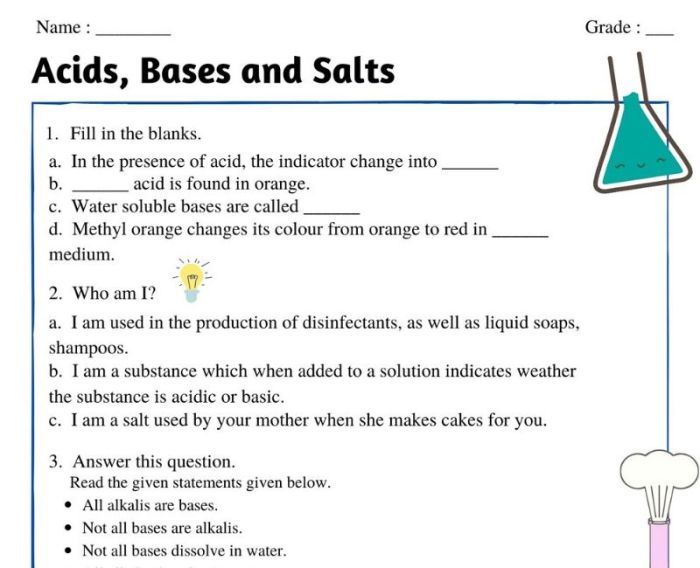
Worksheet acids bases and salts – Embark on a journey through the fascinating world of acids, bases, and salts with this comprehensive worksheet. Delve into their definitions, properties, reactions, and applications, unraveling the intricate relationships that govern these fundamental chemical entities.
From the fundamental principles of acid-base chemistry to their indispensable roles in everyday life, this worksheet provides a thorough exploration of these essential substances.
1. Definition and Properties of Acids, Bases, and Salts
Arrhenius Definition of Acids and Bases
According to the Arrhenius definition, an acid is a substance that dissociates in water to produce hydrogen ions (H+), while a base is a substance that dissociates in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-).
Bronsted-Lowry Definition of Acids and Bases
The Bronsted-Lowry definition defines an acid as a proton donor, while a base is a proton acceptor. This definition is more general than the Arrhenius definition and includes substances that do not dissociate in water.
Lewis Definition of Acids and Bases
The Lewis definition defines an acid as an electron-pair acceptor, while a base is an electron-pair donor. This definition is the most general and includes all types of acids and bases.
Examples of Acids and Bases
- Strong acids: HCl, H2SO4, HNO3
- Weak acids: CH3COOH, H2CO3
- Strong bases: NaOH, KOH, Ca(OH)2
- Weak bases: NH3, pyridine
Properties of Salts
Salts are ionic compounds formed by the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base. They are typically soluble in water and have high electrical conductivity. Salts can be classified as acidic, basic, or neutral depending on the nature of the acid and base that formed them.
2. Chemical Reactions Involving Acids, Bases, and Salts: Worksheet Acids Bases And Salts
Neutralization Reaction
A neutralization reaction is a reaction between an acid and a base that produces salt and water. The reaction is typically exothermic and releases heat.
Precipitation Reaction
A precipitation reaction is a reaction between two soluble salts that produces an insoluble salt that precipitates out of solution. The reaction is typically driven by the formation of a solid product.
Role of Acids and Bases in Redox Reactions
Acids and bases can act as oxidizing or reducing agents in redox reactions. An oxidizing agent is a substance that accepts electrons, while a reducing agent is a substance that donates electrons.
3. Applications of Acids, Bases, and Salts
Uses of Acids in Industry
- Production of fertilizers
- Production of plastics
- Metalworking
Uses of Bases in Everyday Products
- Soaps
- Detergents
- Antacids
Importance of Salts in Living Organisms
Salts play a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of living organisms. They also help regulate blood pressure and nerve function.
4. Safety Considerations When Working with Acids, Bases, and Salts
Potential Hazards, Worksheet acids bases and salts
- Burns
- Eye damage
- Respiratory irritation
Safety Precautions
- Wear protective clothing, including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Handle acids and bases with care.
- Dispose of acids and bases properly.
FAQs
What is the difference between an acid and a base?
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water.
What is a salt?
A salt is an ionic compound formed by the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base.
What are some common applications of acids?
Acids are used in a wide range of industrial processes, including the production of fertilizers, plastics, and batteries.
What are some common applications of bases?
Bases are used in everyday products such as soaps, detergents, and paper.
What are some safety precautions to consider when working with acids and bases?
Acids and bases can be corrosive and cause burns. Always wear protective clothing and goggles when handling them.