Match the serous membrane correctly with the definition – Match the serous membrane correctly with its definition: embark on a captivating journey through human anatomy as we delve into the intricacies of these delicate tissues. From their structure and function to their clinical significance, this exercise promises an immersive exploration of the serous membranes, revealing their essential role in maintaining homeostasis and protecting vital organs.
Serous membranes, with their glistening surfaces and remarkable ability to reduce friction, are the unsung heroes of our internal environment. They line body cavities and envelop organs, creating a protective barrier that safeguards against infection and facilitates movement. Join us as we uncover the fascinating world of serous membranes, matching their names to their precise definitions and gaining a deeper understanding of their vital contributions to our overall well-being.
Introduction
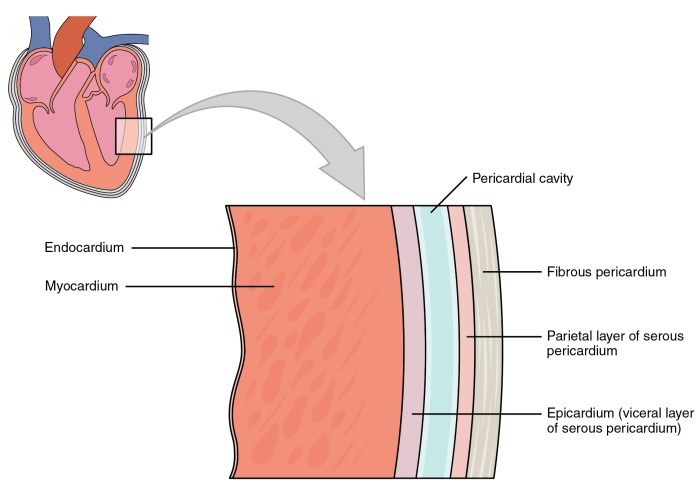
Serous membranes are thin, double-layered tissues that line body cavities and cover internal organs. They play a crucial role in reducing friction and protecting organs from damage. The purpose of this exercise is to match serous membranes with their definitions, enhancing your understanding of their anatomy and significance.
Serous Membranes
A serous membrane consists of two layers: the parietal layer, which lines the body cavity, and the visceral layer, which covers the organ. The space between these layers is filled with serous fluid, which lubricates and cushions the organs.
| Serous Membrane | Location | Associated Organ(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Pleura | Thoracic cavity | Lungs |
| Pericardium | Pericardial cavity | Heart |
| Peritoneum | Abdominal cavity | Stomach, intestines, liver, spleen |
Definitions of Serous Membranes
- Pleura: Serous membrane lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs.
- Pericardium: Serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity and covering the heart.
- Peritoneum: Serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering the organs within.
Matching Exercise: Match The Serous Membrane Correctly With The Definition
| Serous Membrane | Definition |
|---|---|
| Pleura | |
| Pericardium | |
| Peritoneum |
- Serous membrane lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs.
- Serous membrane lining the pericardial cavity and covering the heart.
- Serous membrane lining the abdominal cavity and covering the organs within.
Evaluation
Your responses will be evaluated based on the accuracy of your matches. Correct matches will earn you a point, while incorrect matches will result in no points. To improve your accuracy, review the definitions carefully and pay attention to the location and associated organs of each serous membrane.
Common Queries
What are serous membranes?
Serous membranes are thin, double-layered tissues composed of mesothelium (a layer of simple squamous epithelial cells) and a delicate connective tissue layer. They line body cavities and envelop organs, providing a smooth, moist surface that reduces friction during movement.
What is the function of serous membranes?
Serous membranes serve multiple essential functions: they secrete a lubricating fluid that reduces friction between opposing surfaces, provide a protective barrier against infection, and facilitate the movement of organs within body cavities.
What are the different types of serous membranes?
There are several types of serous membranes, each named according to its location and the organs it covers. Examples include the pleura (lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs), pericardium (surrounding the heart), and peritoneum (lining the abdominal cavity and covering the abdominal organs).