Delving into the realm of phase change graphs, this comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of these graphs, empowering readers with the knowledge to decipher their secrets. Phase change graph worksheet answers lie at the heart of this exploration, illuminating the concepts that govern the behavior of substances as they transition between different states.
Phase change graphs provide a visual representation of the temperature and time changes associated with phase transitions, offering valuable insights into the thermodynamics of these processes. This guide delves into the interpretation of phase change graphs, revealing how to identify different phases of a substance, calculate enthalpy values, and uncover common errors that can arise.
Phase Change Graphs
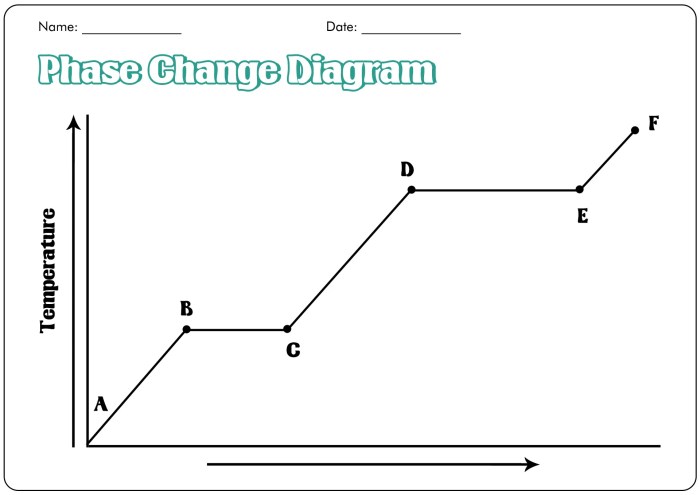
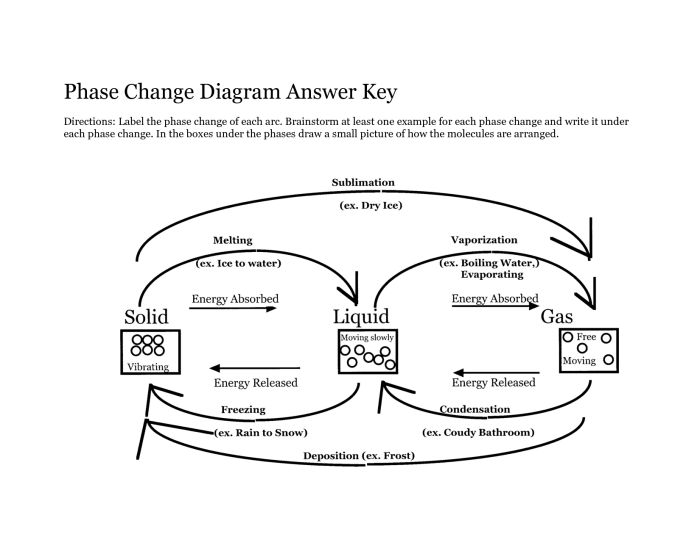
A phase change graph is a graphical representation of the temperature and time changes that occur during a phase change of a substance. Phase changes are physical changes that involve a change in the state of a substance, such as from solid to liquid, liquid to gas, or gas to solid.
Phase change graphs can be used to study the thermodynamics of phase changes and to calculate the enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization of a substance.
Examples of Phase Change Graphs
The following are examples of phase change graphs for different substances:
- Water
- Carbon dioxide
- Iron
Different Sections of a Phase Change Graph, Phase change graph worksheet answers
A phase change graph typically consists of three sections:
- The first section shows the temperature of the substance increasing as it is heated.
- The second section shows the temperature of the substance remaining constant as it undergoes a phase change.
- The third section shows the temperature of the substance increasing again as it continues to be heated.
Interpreting Phase Change Graphs
Temperature and Time Axes
The temperature axis of a phase change graph shows the temperature of the substance. The time axis shows the time it takes for the substance to undergo the phase change.
Phases of a Substance
The different phases of a substance can be identified on a phase change graph by looking at the temperature and time axes. The solid phase is the region of the graph where the temperature is below the melting point. The liquid phase is the region of the graph where the temperature is between the melting point and the boiling point.
The gas phase is the region of the graph where the temperature is above the boiling point.
Enthalpy of Fusion and Enthalpy of Vaporization
The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of heat required to melt a solid substance. The enthalpy of vaporization is the amount of heat required to vaporize a liquid substance. The enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization can be calculated from a phase change graph by measuring the area under the curve.
Applications of Phase Change Graphs: Phase Change Graph Worksheet Answers
Phase change graphs are used in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. They can be used to design and optimize processes involving phase changes, such as heating and cooling systems, refrigeration, and power plants.
Examples of Applications
- Phase change graphs can be used to determine the optimal temperature for a chemical reaction.
- Phase change graphs can be used to design a cooling system for a computer.
- Phase change graphs can be used to optimize the efficiency of a power plant.
Common Errors in Interpreting Phase Change Graphs
There are several common errors that students make when interpreting phase change graphs. These errors include:
- Mistaking the melting point for the boiling point.
- Mistaking the boiling point for the freezing point.
- Not recognizing that the temperature of a substance can remain constant during a phase change.
Reasons for Errors and Strategies to Avoid Them
These errors can be avoided by carefully studying the phase change graph and by understanding the concepts of phase changes.
Incorrect and Correct Interpretations
- Incorrect: The temperature of a substance increases continuously during a phase change.
- Correct: The temperature of a substance remains constant during a phase change.
FAQ Summary
What is a phase change graph?
A phase change graph is a graphical representation of the temperature and time changes associated with a substance undergoing a phase transition, such as melting, freezing, vaporization, or condensation.
How do I interpret a phase change graph?
To interpret a phase change graph, identify the temperature and time axes, and locate the different sections of the graph that correspond to different phases of the substance. The slopes and plateaus in the graph provide information about the enthalpy changes and rates of phase transitions.
What are common errors to avoid when interpreting phase change graphs?
Common errors include misidentifying phase boundaries, incorrectly calculating enthalpy values, and failing to account for external factors that may affect the phase transition process.