In the context of small molecules with similar molar masses, we delve into a fascinating realm where molecular structure, properties, and reactivity intertwine, shaping the behavior and applications of these fundamental building blocks of matter.
From unraveling the intricate relationships between molar mass and physical properties to exploring the impact of intermolecular interactions and spectroscopic techniques, this comprehensive analysis provides a thorough understanding of these molecules and their significance in various scientific disciplines.
Small Molecules with Similar Molar Masses
Small molecules with similar molar masses exhibit intriguing variations in their physical and chemical properties, making their study crucial in various scientific fields. This article explores the unique characteristics, intermolecular interactions, and applications of such molecules, providing a comprehensive understanding of their significance.
1. Physical and Chemical Properties, In the context of small molecules with similar molar masses
Molar mass plays a significant role in determining the physical properties of molecules. Small molecules with similar molar masses tend to have comparable melting points, boiling points, and solubility. However, variations in molecular structure and intermolecular interactions can lead to subtle differences in these properties.
- Melting Point:Molecules with stronger intermolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, require more energy to overcome and melt, resulting in higher melting points.
- Boiling Point:Similarly, molecules with stronger intermolecular interactions have higher boiling points, as more energy is needed to break the intermolecular bonds and transition to the gas phase.
- Solubility:The solubility of small molecules in different solvents depends on the polarity of both the molecule and the solvent. Molecules with similar polarities tend to have similar solubilities.
2. Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. Small molecules with similar molar masses can exhibit various types of structural isomerism.
Types of Structural Isomers:
- Constitutional Isomers:Molecules with the same molecular formula but different atom connectivity.
- Stereoisomers:Molecules with the same molecular formula and atom connectivity but different spatial arrangements of atoms.
Structural isomers have different physical and chemical properties due to variations in their molecular shapes and intermolecular interactions.
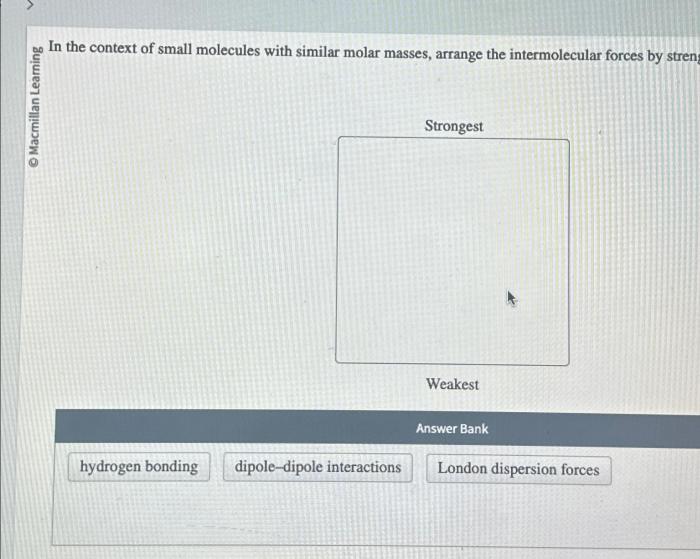
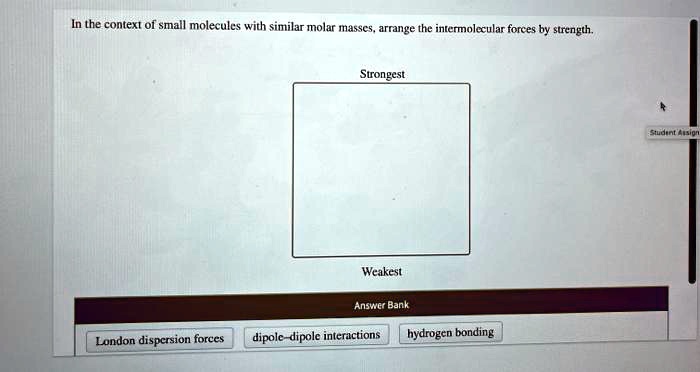
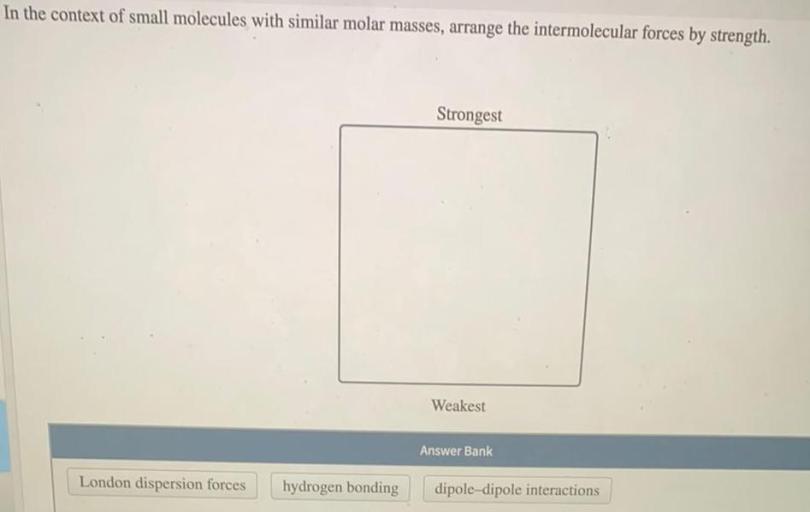
3. Intermolecular Interactions
Intermolecular interactions play a crucial role in shaping the properties of small molecules. The strength and directionality of these interactions determine the physical and chemical behavior of molecules.
Types of Intermolecular Interactions:
- Hydrogen Bonding:Strong dipole-dipole interactions between molecules containing hydrogen atoms bonded to highly electronegative atoms (e.g., O, N, F).
- van der Waals Forces:Weak interactions that include dipole-dipole interactions, London dispersion forces, and induced dipole-dipole interactions.
Small molecules with similar molar masses can exhibit different intermolecular interactions, leading to variations in properties such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility.
Top FAQs: In The Context Of Small Molecules With Similar Molar Masses
What is the significance of molar mass in understanding small molecules?
Molar mass plays a crucial role in determining the physical properties, reactivity, and behavior of small molecules. It influences factors such as melting point, boiling point, solubility, and intermolecular interactions, providing insights into their molecular structure and behavior.
How do structural isomers affect the properties of small molecules?
Structural isomers are molecules with the same molecular formula but different arrangements of atoms. They exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties due to variations in molecular shape, polarity, and intermolecular interactions, highlighting the importance of molecular structure in determining molecular behavior.
What are the key types of intermolecular interactions and how do they impact small molecules?
Intermolecular interactions, such as hydrogen bonding, van der Waals forces, and dipole-dipole interactions, play a significant role in shaping the properties of small molecules. These interactions influence molecular packing, solubility, and reactivity, providing insights into the behavior of molecules in different environments.